Web scraping is often necessary for gathering data, but building a scraper for every single site can be tedious. What if you could build a single n8n workflow that could be quickly configured to scrape any similar paginated website?
This guide shows you how to create a powerful, reusable web scraping template using n8n, focusing on the configuration of selectors and fields via a simple Input Node.
The Goal: A Configurable & Paginated Scraper
We aim to create a single workflow that iterates through multiple pages and extracts specific data fields (like author and text) using a simple JSON configuration.
Example Site: We will use https://quotes.toscrape.com/tag/humor/ which features two pages of quotes, each containing a set of author and a quote texts.
The Blueprint: Initial Configuration
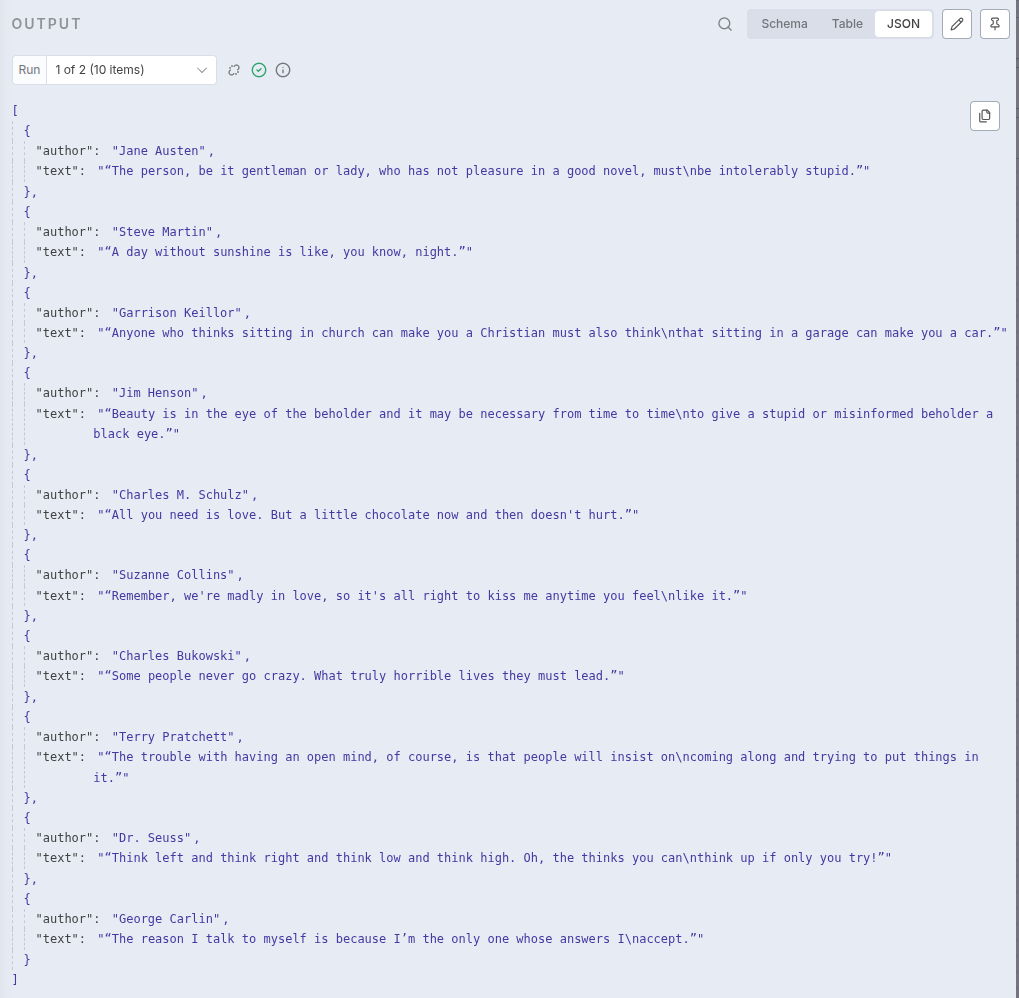
The entire logic of our scraper is defined in the initial Input Node using the following JSON structure. This makes the workflow incredibly easy to reuse—just change this JSON block for a new site!
{
"startUrl": "https://quotes.toscrape.com/tag/humor/",
"nextPageSelector": "li.next a[href]",
"fields": [
{
"name": "author",
"selector": "span > small.author",
"value": "text"
},
{
"name": "text",
"selector": "span.text",
"value": "text"
}
]
}
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
startUrl |
The URL for the first page. |
nextPageSelector |
The CSS selector for the “Next Page” link. |
fields |
An array of items to scrape on each page. |
fields[].name |
The name of item to scrape. |
fields[].selector |
The CSS selector for the specific data point. |
fields[].value |
The HTML property to extract (e.g., text or href). |
Building the Workflow: Step-by-Step
1. Initial Request and Data Preparation
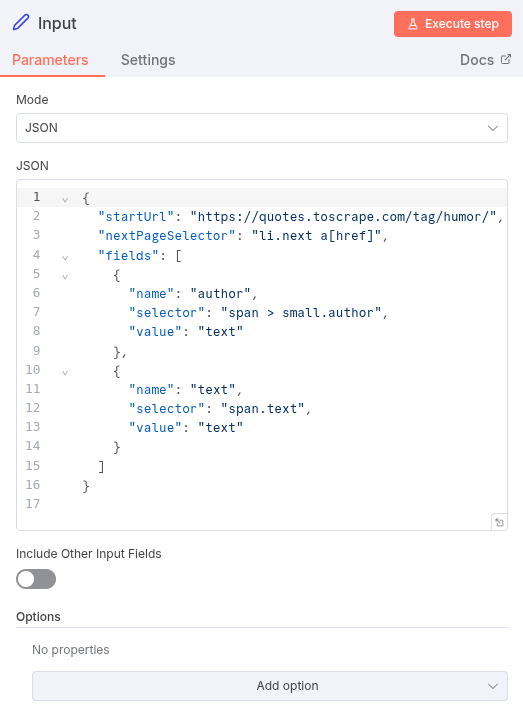
The first step is retrieving the HTML content based on the startUrl provided in our configuration.
- HTTP Request Node: Get the current page’s HTML.
- URL: Use an expression to pull the
startUrlfrom the Input Node:{{ $json.startUrl }} - Response Format: Select
Text.
- URL: Use an expression to pull the
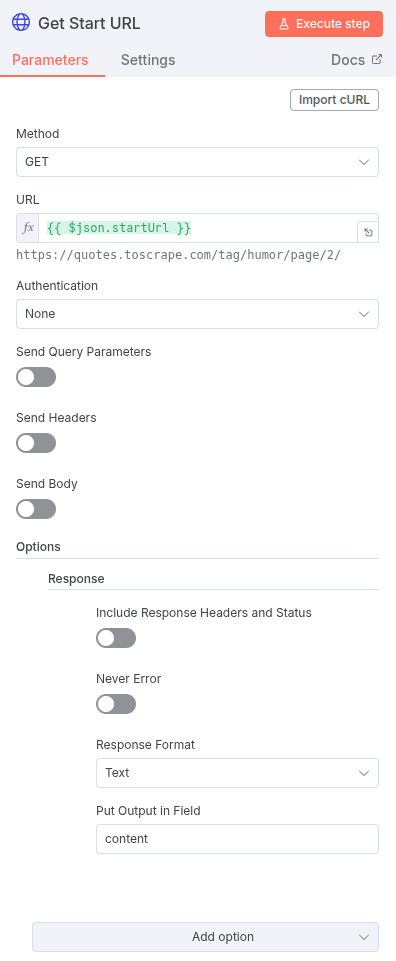
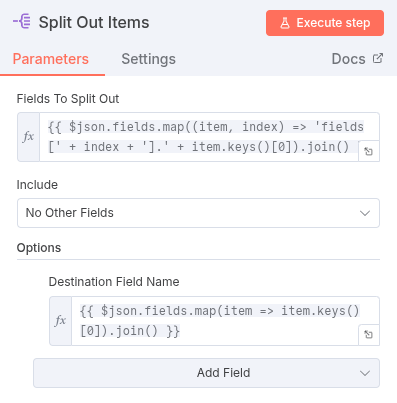
- Split Out Node: Prepare the field configuration for extraction.
- This node takes the
fieldsarray from the Input Node and splits it into multiple individual items (one item for ‘author’ and one for ’text’). - Fields to Split Out:
fields
- This node takes the
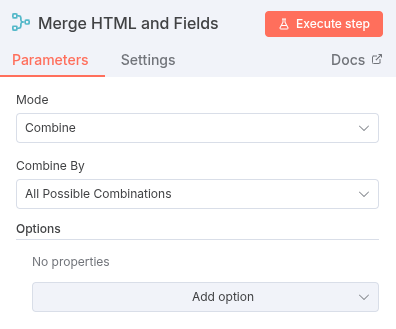
- Merge Node (Combine): Merge the HTML content with the field configurations.
- Mode: Select Combine.
- The node needs two inputs: the HTML content from HTTP Request and the split field items from Split Out.
- This ensures that for every split field item, we have a copy of the HTML content, allowing us to run the HTML extractor for each desired field.
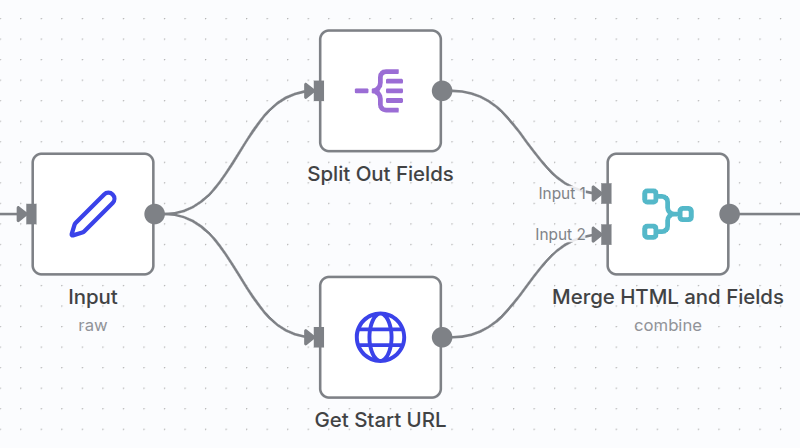
2. Extracting Content
Now that we have the HTML and the field-specific selectors together, we can use the HTML Node to perform the extraction.
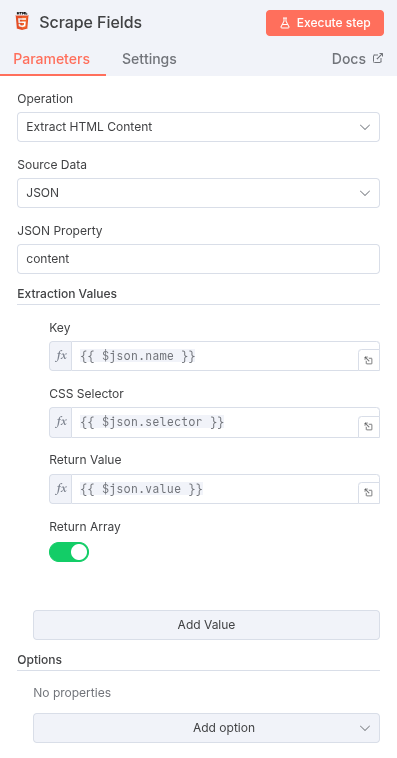
- HTML Node (Extract HTML Content):
- Operation:
Extract HTML Content - Key: Use an expression to pull the field name:
{{ $json.name }} - CSS Selector: Use an expression to pull the field selector:
{{ $json.selector }} - Return Value: Use an expression to pull the value property:
{{ $json.value }}
- Operation:
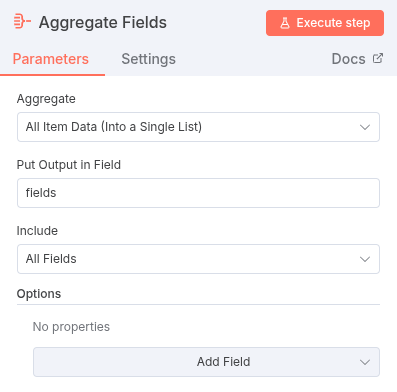
- Aggregate Node: Group the extracted data.
- The HTML node outputs the extracted data, but it’s still grouped by the original
fields(e.g., all authors are one item, all texts are another). - The Aggregate Node collects all items processed so far into a single list.
- The HTML node outputs the extracted data, but it’s still grouped by the original
- Split Out Node:
- To group the resulting author/text pairs, we can use the Split Out Node or a Code Node for more control. For this simple case, the structure after the Aggregate Node might suffice, but for clean output, you may use a Code Node to reorganize the list of authors and texts into objects like
[{author: "A", text: "T"}, ...].
- To group the resulting author/text pairs, we can use the Split Out Node or a Code Node for more control. For this simple case, the structure after the Aggregate Node might suffice, but for clean output, you may use a Code Node to reorganize the list of authors and texts into objects like
3. Implementing Pagination (The Loop)
The key to multi-page scraping is creating a mechanism that repeats the process until the “next page” link is no longer found. This requires a loop structure that updates the original configuration.
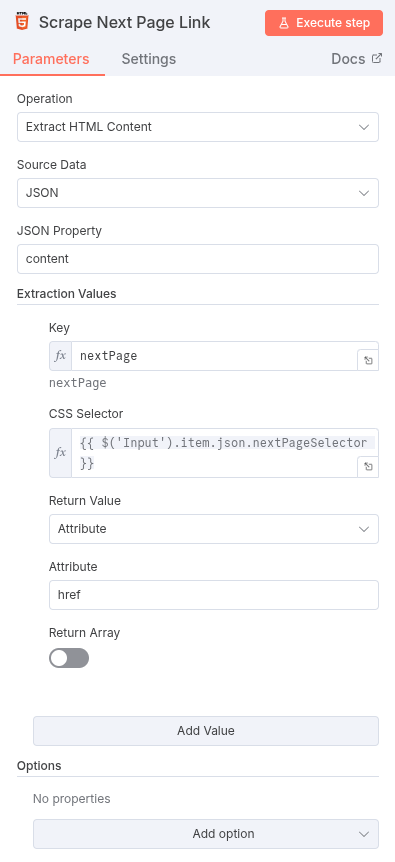
- HTML Node (Extract Next Page Link):
- Before the data splitting, connect a second branch from the
HTTP Request Nodeto a newHTML Node. - Operation:
Extract HTML Content - CSS Selector: Use the configuration value:
{{ $("Input").item.json.nextPageSelector }} - Attribute:
href(to get the URL).
- Before the data splitting, connect a second branch from the
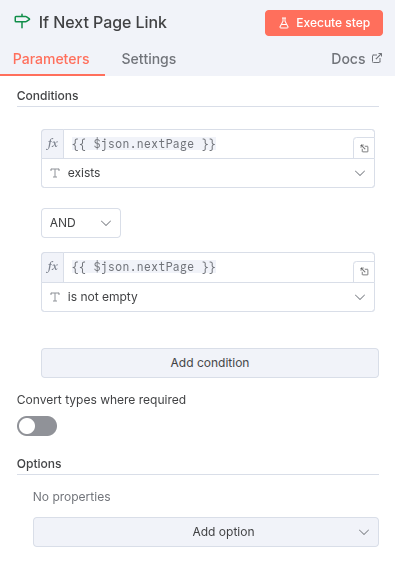
- If Node: Check if a next page link was found.
- Value 1:
{{ $json.nextPage }}(The output of the HTML node) - Condition:
is not empty
- Value 1:
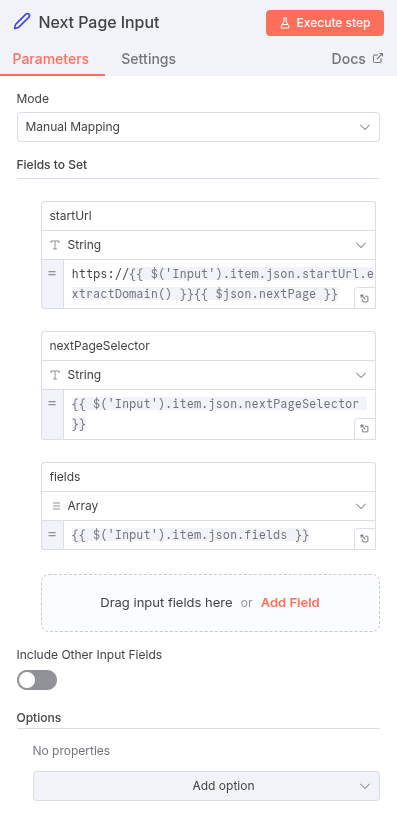
- Set Node (True Branch): Update the startUrl for the next iteration.
- If the link exists, use the Set Node to update the original configuration.
- Value:
{{ $json.nextPage }} - Key:
startUrl(This overwrites the originalstartUrlin the input item).
- Closing the Loop:
- Connect the output of the Set Node directly back to the input of the HTTP Request Node and Split Out Node. This tells n8n to execute the entire scraping branch again, but this time using the newly updated
startUrl. - When the If Node fails (the link is not found), the workflow completes the aggregation of all scraped data.
- Connect the output of the Set Node directly back to the input of the HTTP Request Node and Split Out Node. This tells n8n to execute the entire scraping branch again, but this time using the newly updated
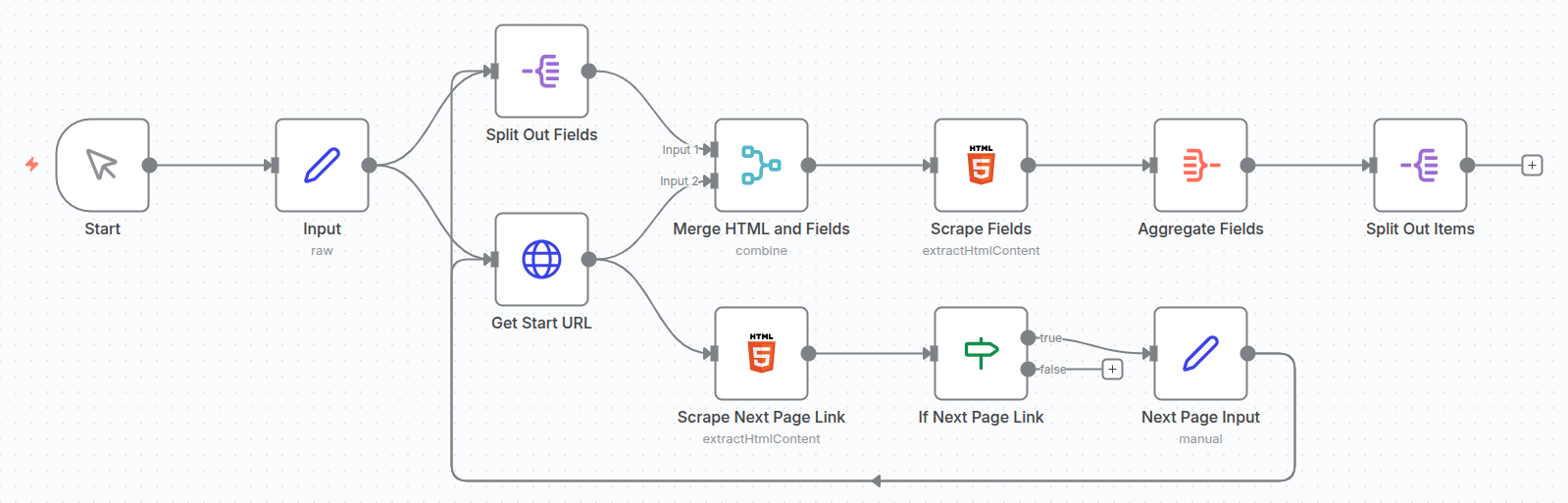
By setting up this dynamic loop, the workflow automatically repeats until all available pages have been visited and their data aggregated. This gives you a truly flexible, one-stop solution for a wide range of web scraping tasks!