In our previous post, we built a simple AI assistant that read an entire Google Sheet every time it needed to “think.” It worked beautifully for 50 items, but what happens when your inventory grows to 500, 5,000, or even 50,000 items?
The answer is RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) using a Vector Database. Instead of feeding the AI the whole book, we only give it the relevant page.
In this guide, we’ll move your inventory logic into Supabase using the pgvector extension, all running on remote environment.
The Architecture: Why Vector Search?
Traditional search looks for exact keywords. Vector search looks for meaning. If a user asks for “compact workstations,” a vector search can find the ASUS NUC 15 Pro+ even if the word “workstation” isn’t in the title, because their mathematical “embeddings” are similar.
Step 1: Preparing the Database (Supabase)
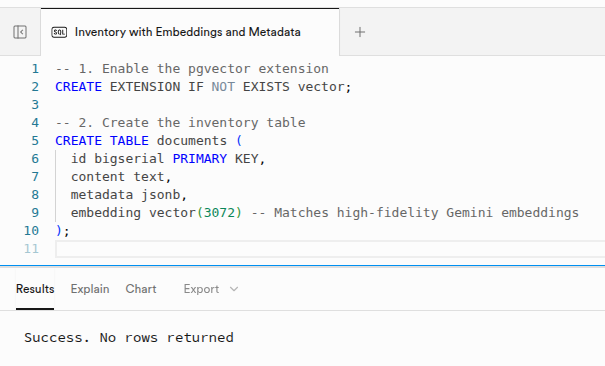
First, we need to turn PostgreSQL into a vector powerhouse. In your Supabase SQL Editor, we create a table that can store 3072-dimension vectors (the standard for high-fidelity Gemini embeddings).
Enable Vector and Create Table
Run this snippet to enable the extension and create the storage for your hardware inventory:
-- 1. Enable the pgvector extension
CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS vector;
-- 2. Create the inventory table
CREATE TABLE documents (
id bigserial PRIMARY KEY,
content text,
metadata jsonb,
embedding vector(3072) -- Matches high-fidelity Gemini embeddings
);
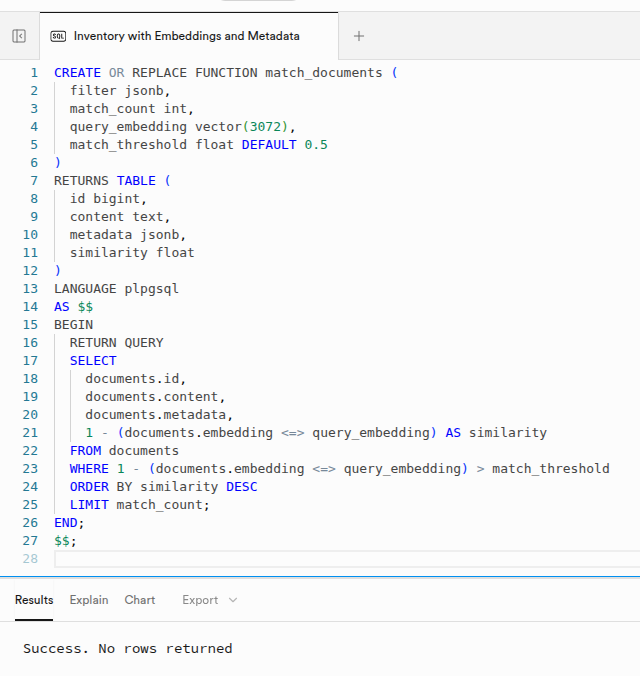
The “Magic” Function
n8n uses a specific function to communicate with Supabase. We must define match_documents to handle the heavy lifting of calculating cosine similarity. This ensures the AI gets the most relevant hardware specs instantly.
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION match_documents (
filter jsonb,
match_count int,
query_embedding vector(3072),
match_threshold float DEFAULT 0.5
)
RETURNS TABLE (
id bigint,
content text,
metadata jsonb,
similarity float
)
LANGUAGE plpgsql
AS $$
BEGIN
RETURN QUERY
SELECT
documents.id,
documents.content,
documents.metadata,
1 - (documents.embedding <=> query_embedding) AS similarity
FROM documents
WHERE 1 - (documents.embedding <=> query_embedding) > match_threshold
ORDER BY similarity DESC
LIMIT match_count;
END;
$$;
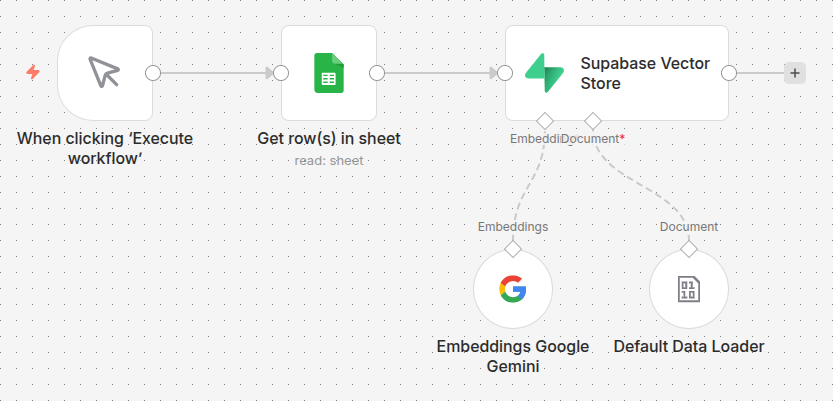
Step 2: Path A - The Sync Workflow (The Indexer)
This workflow runs once (or on a schedule) to turn your Google Sheet rows into vectors.
- Google Sheets: Fetches your list of components (Kingston RAM, BenQ monitors, etc.).
- Supabase Vector Store (Insert): This node takes your text, sends it to Gemini to be “vectorized,” and saves it into the
embeddingcolumn.
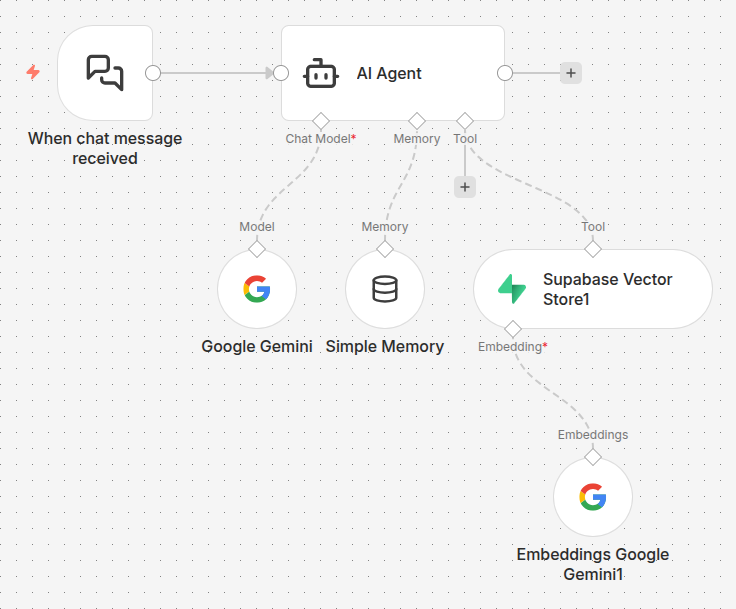
Step 3: Path B - The Chat Workflow (The Retrieval)
Now for the fun part. We build the agent that actually talks to your customers.
- AI Agent + Simple Memory: This provides the “personality” and the “memory” (so it remembers that “it” refers to the Keychron Q6 Max you just mentioned).
- Supabase Vector Tool: This is the most important part. We attach Supabase Vector Store as a Tool. When the user asks a question, the agent sends that question to Supabase, which returns the top 3-5 most relevant items.
Step 4: The System Prompt
The System Prompt is the instruction set that tells the AI how to act as a “Hardware Specialist.” Copy and paste the following into the System Prompt field of your AI Agent node:
You are an expert Hardware Sales Specialist.
Your goal is to help users find the right equipment from our inventory.
INSTRUCTIONS:
1. ALWAYS use the 'inventory_search' tool when a user asks about products,
prices, or availability.
2. If a user asks for a category (e.g., "What monitors do you have?"),
use the tool to find items in that category.
3. Handle technical specifics accurately. If a user mentions a specific
model like 'ASUS NUC 15 Pro+' or 'Keychron Q6 Max', ensure you provide
the exact details found in the tool.
4. Use conversation memory to handle follow-up questions. If the user
asks "How much is it?" or "Is it in stock?", refer to the last item
you both discussed.
5. Provide the Price first in your response. Only mention the exact
stock/quantity if the user explicitly asks about availability.
6. If an item is not found, check for similar items in the same category
or suggest the user checks the spelling.
TONE:
Professional, helpful, and technically knowledgeable.
The Final Result: Real-World Performance
The retrieval happens in milliseconds. Here is how a conversation looks:
- User: “I need a high-end white keyboard.”
- AI: “We have the Keychron Q6 Max Shell White (Jupiter Banana) keyboard for $219.”
- User: “Is it in stock at the moment?”
- AI: “Yes, we have 3 units of the Keychron Q6 Max Shell White (Jupiter Banana) in stock.”

Next Steps: Beyond Retrieval
Now that you have a functioning RAG system, you can:
- Add Real-time Price Tracking: Sync your vectors with live API data.
- Multi-Channel Deployment: Connect this same backend to a Telegram bot for your sales team.
- Self-Healing Sync: Add logic to delete old vectors before inserting new ones to avoid duplicates.
Ready to build the future of your inventory management? Download the n8n template here.
